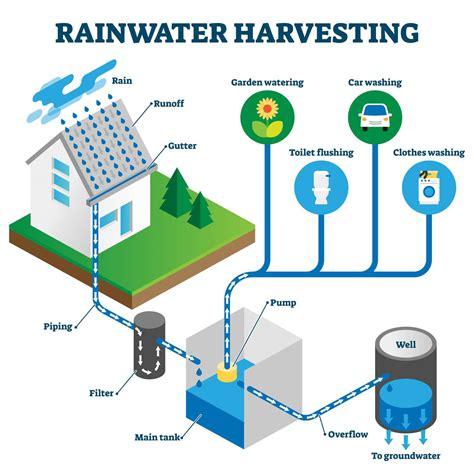
Rainwater harvesting refers to the collection and storage of rainwater for later use, rather than allowing it to flow into drains or evaporate. With water scarcity emerging as a global problem, this technique is increasingly being seen as an environmentally friendly and viable means.
Why Is Rainwater Harvesting Important?
Only roughly 2.5% of water on our planet is freshwater, and most of it is trapped in glaciers or deep within the ground. Rainwater harvesting serves to:
Decrease reliance on groundwater
Save on water bills
Prevent urban flooding
Replenish underground water tables
Supply a secondary water source for non-potable uses and, after proper treatment, even drinking
How Does It Work?
A typical rainwater harvesting system consists of:
Catchment area: Usually a rooftop or open surface where rain is collected
Gutters and pipes: Direct the water to a storage system
Filtration unit: Eliminates leaves, soil, and other contaminants
Storage tank: Stores the purified water
Recharge pit or soakwell (optional): Permits excess water to seep into the earth and replenish aquifers
Types of Rainwater Harvesting
Rooftop Harvesting: Gathers water from roofs of buildings into tanks or underground storage.
Surface Runoff Harvesting: Captures water that overflows land surfaces during rain.
Groundwater Recharge Systems: Flows captured rainwater to wells or pits for replenishing groundwater sources.
Rainwater Harvesting Advantages
Environmentally sound
Safeguards available water supply system
Pivotal during arid or dry conditions
Supports careful usage of water
Prevents waterlogging and erosion of soils
Drawbacks
Needs continuous upkeep to avert contamination
Capital investment could be high during initiation
May be devoid of space or adequate planning in urban spaces
General knowledge among people still lacks understanding about rainwater harvesting in many places
Conclusion
Rainwater harvesting is a simple and effective means of water conservation. By collecting and recycling rainwater, we are able to ease water shortages, save groundwater, and build a more secure environment. With its widespread application, this easy technique can effectively enhance water security for generations to come.