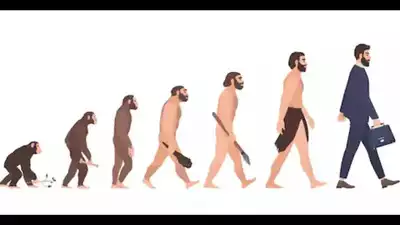
Human evolution is the long and interesting story of how today's humans (Homo sapiens) came to be formed over millions of years. It evolved around 6 to 7 million years ago in Africa, when the first ancestors of ours began evolving from ape-like animals.
The first key step of evolution was walking and standing up on two legs, or to be bipedal. Early humans were therefore able to employ their hands uninhibitedly for hunting and manufacturing tools. With the passage of time, the size of their brains increased, which allowed them to think, learn, and communicate.
Species like Australopithecus, Homo habilis, and Homo erectus made an important contribution to our development. They mastered the use of fire, created stone tools, and lived in settlements. Then came Homo sapiens, which evolved around 300,000 years ago with superior thinking, speech, and imagination.
Human evolution is a tale of survival, adaptation, and intelligence. It illustrates how we developed over time to become the species we are today — with the ability to construct cities, travel to space, and transform the world.