Yes, there is evidence of increased tree growth and expansion globally, although with some caveats. Studies show that there are more trees on Earth now than 35 years ago. This increase is due to various factors, including climate change, reforestation efforts, and trees reclaiming land. However, faster growth due to climate change can also lead to reduced tree density and potentially shorter lifespans.
Factors contributing to tree growth:
Climate change:
Rising temperatures and atmospheric CO2 levels are causing trees to grow faster, especially in temperate regions.
Reforestation efforts:
Large-scale planting of trees by humans is contributing to the overall increase in tree cover.
Land reclamation:
Trees are able to take root and thrive in areas that were previously unsuitable due to human activity or climate change, leading to increased tree cover in these regions.
Consequences of faster tree growth:
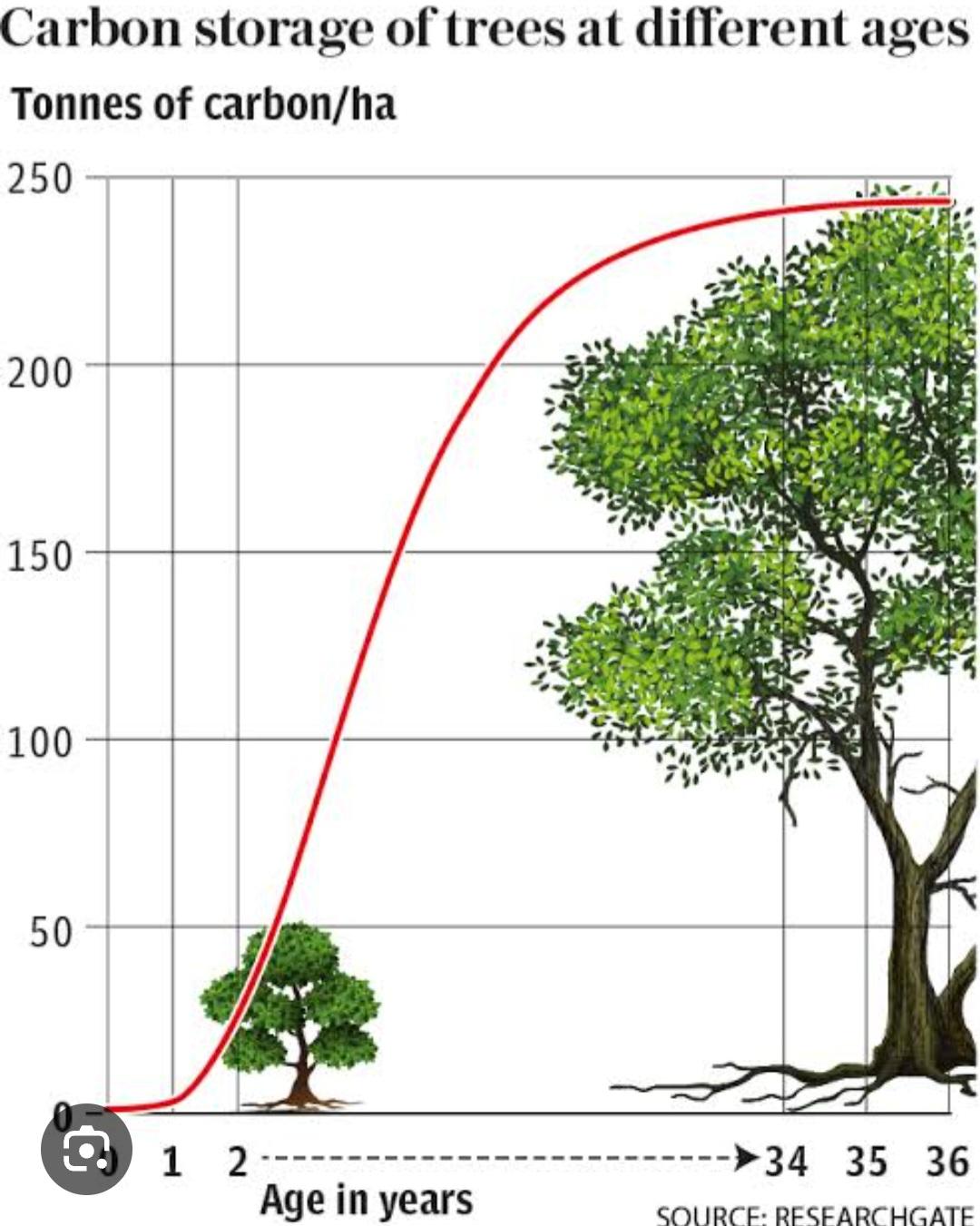
Increased biomass: Faster growth can lead to higher biomass production, potentially increasing carbon storage capacity in forests.
Reduced density: Some trees are growing larger but are also less dense, potentially making them more vulnerable to wind and other stresses.
Shorter lifespans: Faster growth can also lead to shorter lifespans for some trees.